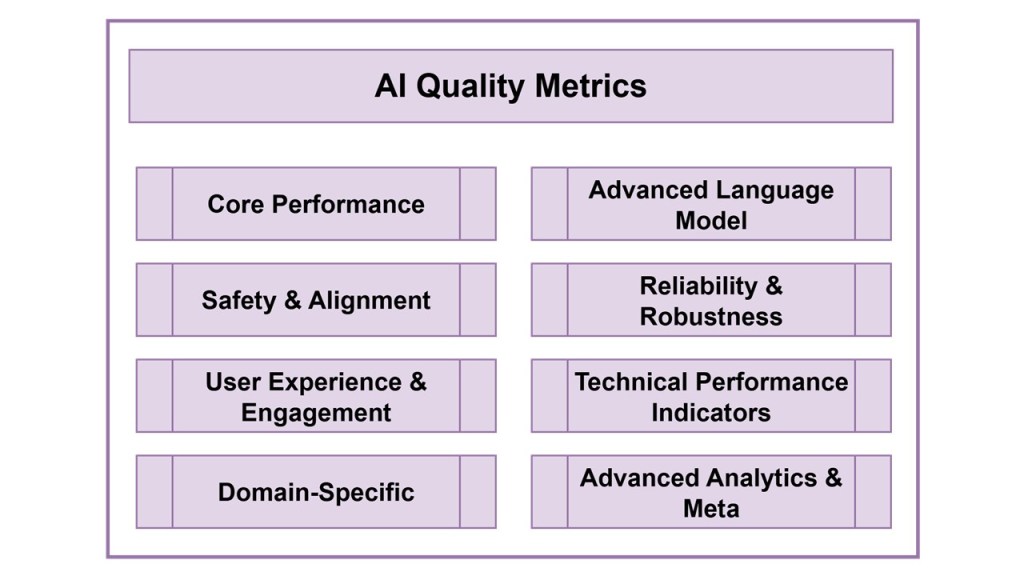
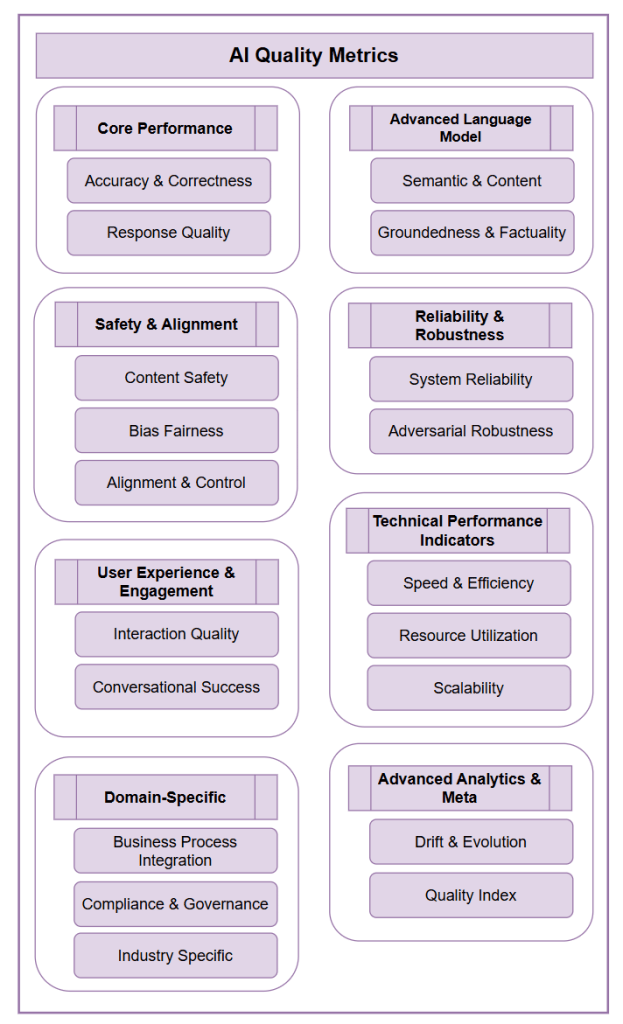
As artificial intelligence becomes the backbone of modern enterprise operations, monitoring the right metrics has never been more critical. While many organizations focus on basic performance indicators, a comprehensive AI quality framework requires tracking dozens of interconnected benchmarks across multiple dimensions.
Link to AI Quality Schema Blog Post: AI Quality Metrics Schema – Ross McNeely
This guide presents the complete landscape of AI metrics that forward-thinking enterprises should monitor to ensure their AI systems deliver reliable, safe, and valuable outcomes.
Core Performance Metrics

Accuracy and Correctness
Accuracy remains the foundation of AI evaluation, measuring how often the system produces correct outputs. However, accuracy alone tells an incomplete story. Enterprises should also track:
- Precision and Recall: Understanding false positives versus false negatives
- F1 Score: Balanced measure combining precision and recall
- Mean Average Precision (mAP): Particularly important for ranking and retrieval systems
- Top-K Accuracy: Measuring if the correct answer appears in the top K predictions
When monitoring AI quality, different metrics serve distinct purposes depending on the model type and application requirements. Precision measures the proportion of positive predictions that are actually correct, making it crucial for applications where false positives are costly, such as fraud detection or medical diagnosis systems. F1Score provides a balanced view by harmonically averaging precision and recall, offering a single metric that accounts for both false positives and false negatives particularly valuable when dealing with imbalanced datasets or when you need to optimize for both precision and recall simultaneously. MeanAveragePrecision(mAP) is essential for ranking and retrieval systems, as it evaluates how well a model orders results by computing the average precision across different recall levels, making it the gold standard for search engines, recommendation systems, and object detection models. Top-K Accuracy measures whether the correct answer appears within the top K predictions, which is particularly relevant for classification tasks where near-misses are acceptable, such as image recognition or natural language processing applications where multiple valid interpretations may exist. Together, these metrics provide a comprehensive framework for evaluating AI systems across different dimensions of performance, ensuring models meet both technical accuracy requirements and real-world application needs.
Response Quality Dimensions
Modern AI systems require nuanced quality assessment beyond simple correctness:
- Coherence: Logical consistency and flow within responses
- Fluency: Natural language quality and readability
- Relevance: How well responses address the actual query or need
- Completeness: Whether responses adequately cover the topic scope
- Conciseness: Appropriate length without unnecessary verbosity
When monitoring the quality of AI-generated text and language models, qualitative metrics provide essential insights that complement traditional quantitative measures. Coherence evaluates whether the generated content maintains logical consistency and clear connections between ideas throughout the response, ensuring that arguments flow naturally and conclusions follow from premises. Fluency assesses the grammatical correctness, natural language flow, and readability of the output, determining whether the text sounds natural to native speakers and adheres to proper linguistic conventions. Relevance measures how well the AI’s response addresses the specific query or task at hand, ensuring the model stays on topic and provides information that directly relates to the user’s needs rather than generating tangential or off-topic content. Completeness determines whether the response adequately covers all necessary aspects of the question or task, identifying gaps where important information may be missing or where the AI has provided only partial answers to complex queries. Conciseness evaluates the efficiency of communication by measuring whether the AI provides the necessary information without unnecessary verbosity, repetition, or filler content that could dilute the core message. These five dimensions work together to create a comprehensive framework for evaluating the practical utility and user experience of AI-generated content, ensuring that models not only produce technically correct outputs but also deliver genuinely helpful and well-crafted responses that meet human communication standards.
Advanced Language Model Metrics

Semantic and Content Quality
- GPT Similarity: Comparing outputs to high-quality reference responses
- Semantic Similarity: Measuring meaning preservation using embedding models
- Content Diversity: Avoiding repetitive or templated responses
- Creativity Index: Measuring novel and innovative response generation
- Contextual Appropriateness: Responses matching the conversational context
When monitoring AI quality in creative and generative applications, specialized metrics capture nuanced aspects of content generation that traditional accuracy measures cannot assess. GPT Similarity measures how closely generated content resembles outputs from established language models, serving as a benchmark for evaluating whether new models achieve comparable performance standards while also identifying potential over-reliance on training patterns. Semantic Similarity evaluates the conceptual alignment between generated content and reference materials or expected outcomes, using embedding-based approaches to determine whether the AI captures the intended meaning even when using different wording or phrasing. Content Diversity tracks the variety and uniqueness of generated outputs across multiple requests, ensuring that AI systems avoid repetitive or formulaic responses and can produce rich, varied content that maintains user engagement and covers different perspectives on topics. Creativity Index quantifies the originality and innovative aspects of generated content by measuring departure from common patterns while still maintaining coherence and usefulness, balancing novelty with practical value. Contextual Appropriateness assesses whether the AI’s tone, style, complexity, and content choices match the specific situation, audience, and purpose of the interaction, ensuring that responses are suitable for their intended context whether formal, casual, technical, or creative. Together, these metrics provide a sophisticated framework for evaluating AI systems that must balance creativity with utility, ensuring that generative models produce content that is not only technically sound but also engaging, appropriate, and genuinely valuable to users across diverse applications.
Groundedness and Factuality
- Groundedness Score: How well responses are supported by provided sources
- Factual Accuracy: Verification against known facts and databases
- Hallucination Rate: Frequency of generating unsupported or false information
- Citation Quality: Accuracy and relevance of referenced sources
- Temporal Accuracy: Correctness of time-sensitive information
When monitoring AI quality in knowledge-intensive applications, truth and reliability metrics are critical for ensuring trustworthy information delivery. Groundedness Score measures how well AI responses are anchored to provided source materials or evidence, evaluating whether claims can be traced back to verifiable information rather than being generated from the model’s parametric knowledge alone. Factual Accuracy assesses the correctness of specific factual statements against verified ground truth, serving as a fundamental measure of whether the AI provides reliable information that users can depend upon for decision-making. Hallucination Rate quantifies the frequency with which AI systems generate plausible-sounding but false or unverifiable information, representing a critical safety metric that helps identify when models fabricate details, statistics, or references that don’t actually exist. Citation Quality evaluates the appropriateness, accuracy, and relevance of sources referenced by the AI, ensuring that when the system attributes information to external sources, those citations are both correct and support the claims being made. Temporal Accuracy measures whether the AI correctly handles time-sensitive information, including the currency of facts, proper sequencing of events, and awareness of when information may have become outdated or superseded. These metrics collectively form a comprehensive framework for evaluating AI reliability in domains where misinformation can have serious consequences, such as healthcare, finance, journalism, and education, ensuring that AI systems maintain the highest standards of truthfulness and can be trusted as reliable sources of information.
Safety and Alignment Metrics

Content Safety
- Toxicity Detection: Identifying harmful, offensive, or inappropriate content
- Hate Speech Classification: Detecting discriminatory language
- Violence and Self-Harm Indicators: Flagging potentially dangerous content
- Sexual Content Detection: Identifying inappropriate sexual material
- Profanity and Vulgarity Scores: Measuring inappropriate language use
When monitoring AI quality in user-facing applications, safety and content moderation metrics are essential for maintaining responsible deployment and protecting users from harmful content. Toxicity Detection measures the presence of hostile, aggressive, or inflammatory language that could contribute to negative user experiences or online harassment, serving as a primary filter for maintaining civil discourse in AI interactions. Hate Speech Classification identifies content that targets individuals or groups based on protected characteristics such as race, religion, gender, or sexual orientation, ensuring AI systems don’t perpetuate discrimination or amplify harmful stereotypes. Violence and Self-Harm Indicators detect content that glorifies, encourages, or provides instructions for violent acts or self-destructive behaviors, representing critical safety measures that can help prevent real-world harm, particularly for vulnerable users. Sexual Content Detection identifies inappropriate sexual material to ensure age-appropriate interactions and compliance with platform policies, protecting minors and maintaining professional standards in various applications. Profanity and Vulgarity Scores track the use of offensive language and crude expressions, allowing organizations to maintain appropriate tone and register for their specific audience and context. Together, these metrics form a comprehensive content safety framework that enables AI developers to proactively identify and mitigate harmful outputs before they reach users, ensuring that AI systems contribute positively to digital environments while adhering to ethical guidelines, legal requirements, and community standards across diverse applications from educational tools to customer service platforms.
Bias and Fairness
- Demographic Bias: Performance variations across different groups
- Cultural Sensitivity: Appropriateness across cultural contexts
- Gender Bias: Equal treatment regardless of gender references
- Racial and Ethnic Fairness: Consistent quality across diverse populations
- Socioeconomic Bias: Fair treatment across different economic contexts
When monitoring AI quality for ethical deployment, fairness and bias metrics are fundamental for ensuring equitable treatment across diverse user populations and preventing the perpetuation of societal inequalities. Demographic Bias measures whether AI systems produce systematically different outcomes or quality of responses based on user demographic characteristics, ensuring that performance remains consistent regardless of age, location, or other personal attributes. Cultural Sensitivity evaluates how well AI systems respect and appropriately respond to different cultural contexts, traditions, and worldviews, preventing the imposition of dominant cultural assumptions while fostering inclusive interactions that acknowledge diverse perspectives and practices. Gender Bias specifically tracks disparities in how AI systems treat, represent, or respond to different genders, identifying issues such as occupational stereotyping, differential language use, or unequal representation in generated content. Racial and Ethnic Fairness measures whether AI outputs demonstrate equitable treatment across different racial and ethnic groups, detecting both overt discrimination and subtle biases that might manifest in language patterns, assumptions, or quality of assistance provided. Socioeconomic Bias assesses whether AI systems make assumptions or provide different levels of service based on perceived economic status, educational background, or social class indicators. These metrics collectively form a critical framework for responsible AI development, enabling organizations to identify and remediate biases that could harm marginalized communities, ensure compliance with anti-discrimination laws, and build AI systems that serve all users fairly regardless of their background or identity, ultimately contributing to more just and equitable technological advancement.
Alignment and Control
- Refusal Appropriateness: Correctly declining harmful requests without over-refusal
- Instruction Following: Adherence to explicit user instructions
- Behavioral Consistency: Maintaining consistent personality and approach
- Value Alignment: Responses reflecting organizational values and ethics
When monitoring AI quality for alignment and behavioral reliability, these metrics ensure that AI systems operate consistently with intended design principles and user expectations. Refusal Appropriateness evaluates whether AI systems correctly decline inappropriate, harmful, or out-of-scope requests while still being helpful for legitimate use cases, striking the critical balance between safety and utility by saying “no” when necessary without being overly restrictive. Instruction Following measures how accurately AI systems comprehend and execute user instructions across varying levels of complexity and ambiguity, ensuring that models can reliably interpret intent and deliver outputs that match specific requirements, formats, or constraints provided by users. Behavioral Consistency tracks whether AI systems maintain stable response patterns and decision-making approaches across similar contexts and repeated interactions, preventing erratic behavior that could undermine user trust or create unpredictable outcomes in production environments. Value Alignment assesses how well AI behavior reflects intended ethical principles, organizational values, and societal norms, ensuring that systems act in accordance with human values and moral frameworks rather than optimizing purely for task completion without regard for broader implications. Together, these metrics form a comprehensive framework for evaluating AI reliability and trustworthiness, ensuring that systems not only perform their technical functions effectively but also behave in predictable, appropriate, and ethically sound ways that align with human expectations and organizational objectives across diverse applications and use cases.
Reliability and Robustness Metrics
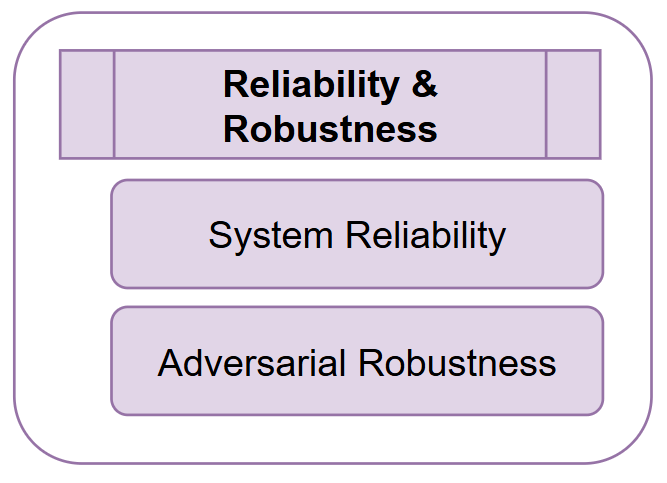
System Reliability
- Consistency Score: Similar outputs for identical inputs across sessions
- Reproducibility: Ability to generate similar results under same conditions
- Stability: Performance maintenance over time and usage
- Error Rate: Frequency of system failures or nonsensical outputs
- Graceful Degradation: Performance under suboptimal conditions
When monitoring AI quality in production environments, robustness and reliability metrics are essential for ensuring consistent performance under varying conditions and maintaining system dependability. Consistency Score measures the degree to which AI systems produce similar outputs when given identical or semantically equivalent inputs, ensuring predictable behavior that users and downstream systems can rely upon for stable operations. Reproducibility evaluates whether AI results can be replicated across different runs, environments, or system configurations, serving as a critical validation measure for scientific applications and debugging processes where consistent outcomes are paramount. Stability tracks how well AI performance persists across different operating conditions, data distributions, and time periods, identifying potential drift or degradation that could compromise system reliability in real-world deployments. Error Rate quantifies the frequency of incorrect outputs, failures, or system malfunctions, providing a fundamental measure of system reliability that directly impacts user experience and operational effectiveness. Graceful Degradation assesses how well AI systems maintain partial functionality and provide meaningful responses when encountering challenging inputs, resource constraints, or edge cases, rather than failing completely or producing nonsensical outputs. These metrics collectively form a comprehensive framework for evaluating AI system robustness, enabling organizations to identify potential points of failure, optimize system resilience, and ensure that AI applications maintain acceptable performance levels even under adverse conditions, ultimately supporting reliable deployment in mission-critical applications where consistency and dependability are essential for user trust and operational success.
Adversarial Robustness
- Prompt Injection Resistance: Resilience against malicious prompt manipulation
- Jailbreak Attempts: Defense against attempts to bypass safety measures
- Edge Case Handling: Performance with unusual or boundary inputs
- Noise Tolerance: Maintaining quality with imperfect or corrupted inputs
- Stress Testing Results: Performance under high load or difficult scenarios
When monitoring AI quality for security and resilience, adversarial robustness metrics are crucial for ensuring systems can withstand malicious attacks and handle challenging operational conditions. Prompt Injection Resistance measures how well AI systems maintain their intended behavior when users attempt to manipulate responses through carefully crafted inputs designed to override system instructions or extract sensitive information, serving as a frontline defense against social engineering attacks. Jailbreak Attempts tracks the system’s ability to resist sophisticated efforts to bypass safety guardrails, content policies, or operational boundaries, ensuring that malicious users cannot exploit conversational techniques to access prohibited functionality or generate harmful content. Edge Case Handling evaluates how AI systems respond to unusual, ambiguous, or boundary conditions that fall outside typical training scenarios, measuring whether the system fails gracefully or produces unexpected behaviors when encountering rare or challenging inputs. Noise Tolerance assesses system performance when inputs contain errors, typos, formatting issues, or other forms of corruption, ensuring that minor imperfections in user queries don’t disproportionately degrade output quality or system functionality. Stress Testing Results measure AI performance under extreme conditions such as high concurrent usage, resource constraints, or deliberately adversarial scenarios designed to push system limits and identify breaking points. Together, these metrics form a comprehensive security and resilience framework that enables organizations to identify vulnerabilities, strengthen system defenses, and ensure that AI applications remain secure, stable, and reliable even when facing sophisticated attacks or operating under challenging conditions that could compromise performance or safety.
User Experience and Engagement Metrics

Interaction Quality
- User Satisfaction: Direct feedback and rating scores
- Task Completion Rate: Success in helping users achieve their goals
- Engagement Duration: Time users spend interacting with the system
- Return Usage Rate: Frequency of users coming back to the system
- Escalation Rate: How often users need to seek human assistance
When monitoring AI quality from a user experience perspective, behavioral and satisfaction metrics provide critical insights into real-world system effectiveness and adoption success. User Satisfaction measures subjective user assessments of AI interactions through surveys, ratings, and feedback mechanisms, capturing whether users find the system helpful, trustworthy, and pleasant to interact with beyond technical performance metrics. Task Completion Rate tracks the percentage of user interactions where the AI successfully helps users achieve their intended goals, serving as a direct measure of practical utility that reflects whether the system delivers meaningful value in real-world scenarios. Engagement Duration analyzes how long users actively interact with the AI system during sessions, providing insights into user interest, content quality, and system usability while identifying patterns that indicate either high engagement or user frustration leading to early abandonment. Return Usage Rate measures user retention by tracking how frequently users come back to the system over time, serving as a strong indicator of perceived value and satisfaction that reflects whether the AI consistently meets user needs across multiple interactions. Escalation Rate quantifies how often users need to seek human assistance, alternative solutions, or escalate issues when the AI cannot adequately address their needs, indicating both system limitations and user frustration points that require attention. These metrics collectively form a comprehensive framework for evaluating AI success from the user’s perspective, enabling organizations to understand not just whether their systems work technically, but whether they create positive user experiences that drive adoption, satisfaction, and long-term value in real-world applications.
Conversational Excellence
- Context Retention: Maintaining relevant information across long conversations
- Turn-Taking Appropriateness: Natural conversation flow and timing
- Clarification Seeking: Asking appropriate questions when input is unclear
- Empathy and Tone: Appropriate emotional response and communication style
- Personalization Quality: Adapting responses to individual user preferences
When monitoring AI quality in conversational and interactive applications, dialogue and interaction metrics assess how naturally and effectively AI systems engage in multi-turn conversations and relationship-building with users. Context Retention measures the AI’s ability to maintain and appropriately reference information from earlier parts of a conversation, ensuring coherent dialogue flow and preventing repetitive questions or contradictory statements that break conversational continuity. Turn-Taking Appropriateness evaluates whether the AI responds at suitable moments, provides adequate response length, and maintains proper conversational rhythm without being overly verbose or abruptly ending interactions when users expect continued engagement. Clarification Seeking tracks how effectively the AI identifies ambiguous or incomplete user inputs and asks targeted follow-up questions to better understand user intent, demonstrating conversational intelligence that enhances task completion rather than making incorrect assumptions. Empathy and Tone assesses whether the AI responds with appropriate emotional sensitivity, matching its communication style to user emotions and situational context while maintaining supportive, respectful, and contextually suitable language throughout interactions. Personalization Quality measures how well the AI adapts its responses to individual user preferences, communication styles, expertise levels, and specific needs without compromising privacy or making inappropriate assumptions about user characteristics. Together, these metrics form a comprehensive framework for evaluating conversational AI effectiveness, ensuring that systems not only provide accurate information but also create engaging, natural, and personally relevant interactions that build user trust and satisfaction through human-like dialogue capabilities that enhance rather than hinder the user experience.
Technical Performance Indicators
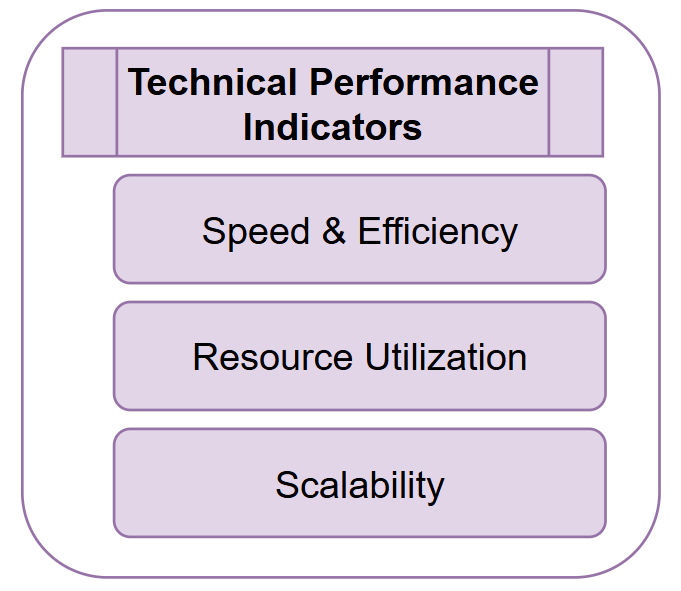
Speed and Efficiency
- Response Latency: Time between input and output generation
- Throughput: Requests processed per unit time
- Time to First Token: Initial response speed for streaming applications
- Processing Speed: Tokens or operations processed per second
- Queue Time: Waiting time during high-demand periods
When monitoring AI quality in production environments, performance and efficiency metrics are essential for ensuring systems meet user expectations and operational requirements for responsiveness and scalability. Response Latency measures the total time from when a user submits a query until they receive a complete response, serving as the primary indicator of user experience quality since delays directly impact satisfaction and system usability across applications. Throughput quantifies how many requests the AI system can process within a given time period, indicating system capacity and scalability potential while helping organizations understand resource requirements for handling concurrent users and peak demand scenarios. Time to First Token tracks the delay before the AI begins generating its response, which is particularly critical for streaming applications where users expect immediate feedback that the system is processing their request, even if the full response takes longer to complete. Processing Speed measures the rate at which the AI generates content once it begins responding, typically measured in tokens or words per second, indicating the efficiency of the underlying computational processes and model inference capabilities. Queue Time captures delays caused by system load and resource contention when multiple requests compete for processing resources, helping identify bottlenecks and capacity constraints that could degrade user experience during high-traffic periods. These metrics collectively form a comprehensive performance monitoring framework that enables organizations to optimize system architecture, allocate computational resources effectively, and ensure that AI applications deliver responsive user experiences while maintaining cost-effective operations at scale.
Resource Utilization
- Computational Cost: Processing power required per interaction
- Memory Usage: RAM consumption during operation
- Energy Efficiency: Power consumption per operation
- Storage Requirements: Data and model storage needs
- Bandwidth Usage: Network resources consumed
When monitoring AI quality from an operational perspective, resource utilization metrics are critical for ensuring sustainable and cost-effective deployment while maintaining performance standards across varying scales of operation. Computational Cost measures the processing power and associated expenses required to generate AI responses, enabling organizations to optimize model efficiency, predict operational budgets, and make informed decisions about hardware investments and cloud service allocations. Memory Usage tracks the RAM and storage requirements during AI inference and training processes, identifying potential bottlenecks that could limit system scalability or require hardware upgrades to maintain responsive performance under increasing user loads. Energy Efficiency quantifies the power consumption per unit of AI output, becoming increasingly important for environmental sustainability goals and operational cost management, particularly in large-scale deployments where energy costs represent significant operational expenses. Storage Requirements measures the disk space needed for model parameters, training data, user interactions, and system logs, helping organizations plan data management strategies and storage infrastructure that can accommodate growing datasets and model complexity over time. Bandwidth Usage tracks network traffic generated by AI systems, including data transfer for distributed processing, user interactions, and cloud-based deployments, ensuring that network infrastructure can support system requirements without creating communication bottlenecks. Together, these metrics form a comprehensive resource monitoring framework that enables organizations to balance AI performance with operational efficiency, supporting sustainable scaling strategies that optimize both user experience and cost-effectiveness while identifying opportunities for system optimization and infrastructure planning.
Scalability Metrics
- Concurrent User Capacity: Maximum simultaneous users supported
- Load Balancing Effectiveness: Performance under distributed load
- Auto-scaling Response: System adaptation to demand changes
- Fault Tolerance: Continued operation during component failures
- Recovery Time: Speed of restoration after system issues
When monitoring AI quality in enterprise and high-availability environments, scalability and infrastructure metrics are essential for ensuring systems can reliably serve growing user bases while maintaining consistent performance and uptime standards. Concurrent User Capacity measures the maximum number of simultaneous users the AI system can support without performance degradation, providing critical insights for capacity planning and identifying when infrastructure scaling becomes necessary to maintain service quality. Load Balancing Effectiveness evaluates how well the system distributes computational workload across multiple servers or processing units, ensuring optimal resource utilization and preventing individual components from becoming bottlenecks that could compromise overall system performance. Auto-scaling Response tracks how quickly and accurately the system can automatically adjust computational resources in response to changing demand patterns, measuring both the speed of scaling decisions and the appropriateness of resource allocation to maintain consistent user experience during traffic fluctuations. Fault Tolerance assesses the system’s ability to continue operating when individual components fail, measuring redundancy effectiveness and graceful degradation capabilities that prevent complete service outages from isolated hardware or software failures. Recovery Time quantifies how quickly the system can restore full functionality after experiencing failures, outages, or maintenance events, serving as a critical measure of business continuity and user impact during service disruptions. These metrics collectively form a comprehensive infrastructure resilience framework that enables organizations to build and maintain AI systems capable of supporting mission-critical applications with enterprise-grade reliability, ensuring consistent service delivery even as user demand scales and operational challenges arise.
Domain-Specific Quality Measures

Business Process Integration
- Workflow Integration Success: Seamless operation within existing processes
- Data Pipeline Quality: Accuracy of data processing and transformation
- Decision Support Effectiveness: Quality of insights for business decisions
- Automation Success Rate: Percentage of tasks successfully automated
- Process Improvement Metrics: Efficiency gains from AI implementation
When monitoring AI quality in business and operational contexts, integration and workflow metrics evaluate how effectively AI systems enhance organizational processes and deliver tangible value within existing business ecosystems. Workflow Integration Success measures how seamlessly AI systems connect with existing business processes, applications, and data sources, ensuring that AI capabilities enhance rather than disrupt established operational workflows while maintaining data consistency and process reliability. Data Pipelines Quality assesses the accuracy, completeness, and timeliness of data flows between AI systems and other organizational tools, monitoring data transformation processes, synchronization effectiveness, and the integrity of information exchanges that support decision-making and operational activities. Decision Support Effectiveness evaluates how well AI recommendations and insights actually improve business outcomes, measuring the accuracy of AI-generated suggestions, their adoption rates by human decision-makers, and the resulting impact on key performance indicators and strategic objectives. Automation Success Rate tracks the percentage of routine tasks and processes that AI systems can successfully complete without human intervention, quantifying efficiency gains and identifying areas where automation reduces manual workload while maintaining quality standards. Process Improvement Metrics measure the broader organizational benefits of AI implementation, including productivity increases, error reduction, cost savings, and cycle time improvements that demonstrate the system’s contribution to operational excellence and competitive advantage. Together, these metrics form a comprehensive framework for evaluating AI’s business value and operational impact, ensuring that AI investments deliver measurable returns through improved efficiency, enhanced decision-making, and streamlined processes that support organizational goals and strategic objectives.
Compliance and Governance
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to industry-specific regulations
- Data Privacy Protection: Safeguarding sensitive information
- Audit Trail Completeness: Comprehensive logging for accountability
- Policy Adherence: Following organizational guidelines and standards
- Transparency Score: Explainability and interpretability of decisions
When monitoring AI quality in regulated industries and governance-sensitive applications, compliance and transparency metrics are fundamental for ensuring systems meet legal requirements, ethical standards, and organizational accountability obligations. Regulatory Compliance measures adherence to industry-specific laws and regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, financial services regulations, or sector-specific AI governance frameworks, ensuring that AI systems operate within legal boundaries and maintain necessary certifications for their intended use cases. Data Privacy Protection evaluates how effectively AI systems safeguard personal and sensitive information throughout data collection, processing, and storage lifecycles, tracking encryption implementation, access controls, data minimization practices, and user consent management to prevent privacy breaches and unauthorized data exposure. Audit Trail Completeness assesses whether AI systems maintain comprehensive logs of decisions, data access, model changes, and user interactions that can support regulatory investigations, internal reviews, and accountability processes, ensuring sufficient documentation for compliance verification and incident analysis. Policy Adherence measures how consistently AI systems follow organizational policies, ethical guidelines, and operational procedures, tracking deviations from established protocols and ensuring that AI behavior aligns with institutional values and governance frameworks. Transparency Score quantifies the explainability and interpretability of AI decisions, measuring how well systems can provide clear rationales for their outputs, enable human understanding of decision processes, and support requirements for algorithmic transparency in regulated environments. Together, these metrics form a critical governance framework that enables organizations to deploy AI systems responsibly while meeting legal obligations, maintaining stakeholder trust, and supporting ethical AI practices that protect both users and organizations from compliance risks and reputational damage.
Industry-Specific Metrics
Different sectors require specialized metrics:
Healthcare: Clinical accuracy, patient safety indicators, diagnostic confidence Finance: Fraud detection rates, risk assessment accuracy, regulatory compliance Legal: Citation accuracy, precedent relevance, confidentiality maintenance Education: Learning outcome support, age-appropriateness, curriculum alignment Customer Service: Resolution rates, customer satisfaction, issue escalation accuracy
Advanced Analytics and Meta-Metrics

Drift and Evolution Tracking
- Model Drift Detection: Changes in performance over time
- Data Drift Monitoring: Shifts in input data characteristics
- Concept Drift: Changes in underlying relationships
- Performance Degradation: Decline in quality metrics over time
- Adaptation Effectiveness: Success of model updates and retraining
When monitoring AI quality in dynamic operational environments, drift and adaptation metrics are essential for maintaining system performance as real-world conditions evolve over time and diverge from original training assumptions. Model Drift Detection identifies when AI system behavior changes unexpectedly due to software updates, configuration modifications, or infrastructure changes, ensuring that intentional system modifications don’t introduce unintended performance regressions or behavioral inconsistencies that could compromise reliability. Data Drift Monitoring tracks statistical changes in input data distributions compared to training datasets, detecting shifts in user behavior, environmental conditions, or data sources that could reduce model accuracy and require intervention to maintain performance standards. Concept Drift measures changes in the underlying relationships between inputs and desired outputs, identifying when the fundamental patterns the AI learned during training no longer apply to current conditions, such as evolving user preferences or changing business contexts that alter what constitutes correct responses. Performance Degradation quantifies declining accuracy, efficiency, or user satisfaction metrics over time, providing early warning signals that system performance is deteriorating and enabling proactive maintenance before problems significantly impact user experience or business outcomes. Adaptation Effectiveness evaluates how successfully AI systems adjust to detected changes through retraining, fine-tuning, or other update mechanisms, measuring whether interventions restore performance levels and how quickly systems can adapt to new conditions while maintaining stability. Together, these metrics form a comprehensive monitoring framework for AI systems operating in evolving environments, enabling organizations to maintain reliable performance through proactive detection of changes and effective adaptation strategies that ensure long-term system viability and continued value delivery.
Quality Index Composition
- Composite Quality Score: Weighted combination of multiple metrics
- Quality Trend Analysis: Performance trajectory over time
- Benchmark Comparison: Performance relative to industry standards
- Improvement Velocity: Rate of quality enhancement
- Quality Prediction: Forecasting future performance trends
When monitoring AI quality at an organizational level, aggregated analytics and strategic metrics provide comprehensive insights that enable data-driven decision-making and long-term system optimization across multiple dimensions of performance. Composite Quality Score combines multiple individual metrics into unified indicators that provide holistic assessments of overall AI system health, enabling stakeholders to quickly understand system status and compare performance across different models, time periods, or deployment environments without getting overwhelmed by granular details. Quality Trend Analysis examines patterns and trajectories in AI performance over time, identifying whether systems are improving, degrading, or maintaining stable performance levels while revealing seasonal variations, usage-related patterns, or gradual shifts that require strategic attention or intervention. Benchmark Comparison evaluates AI system performance against industry standards, competitor capabilities, or internal baseline models, providing context for understanding whether current performance levels meet market expectations and identifying areas where systems excel or lag behind established benchmarks. Improvement Velocity measures the rate at which AI systems enhance their performance through updates, training, or optimization efforts, quantifying the effectiveness of development investments and helping organizations allocate resources toward the most impactful improvement initiatives. Quality Prediction uses historical performance data and trend analysis to forecast future system behavior and potential quality issues, enabling proactive planning and resource allocation while identifying when preventive maintenance or system updates will be necessary to maintain desired performance levels. Together, these metrics form a strategic monitoring framework that transforms tactical quality measurements into actionable business intelligence, supporting executive decision-making, resource planning, and continuous improvement initiatives that ensure AI systems deliver sustained value and competitive advantage over time.
Implementation Strategy and Best Practices
Metric Selection Framework
Not all metrics apply to every use case. Consider:
- Business Objectives: Align metrics with organizational goals
- Risk Tolerance: Emphasize safety metrics for high-risk applications
- User Experience Priority: Weight user-facing metrics appropriately
- Technical Constraints: Consider available computing and monitoring resources
- Regulatory Requirements: Include mandatory compliance metrics
Monitoring Infrastructure
Effective metric tracking requires:
- Real-time Dashboards: Live monitoring of critical metrics
- Automated Alerting: Immediate notification of threshold breaches
- Historical Analysis: Trend tracking and pattern recognition
- A/B Testing Capabilities: Comparative performance evaluation
- Integration Tools: Connection with existing monitoring systems
Continuous Improvement Cycle
Establish processes for:
- Regular Metric Review: Periodic assessment of relevance and accuracy
- Threshold Adjustment: Updating benchmarks based on performance data
- New Metric Introduction: Adding measures as systems evolve
- Stakeholder Communication: Clear reporting to business leaders
- Action Planning: Converting insights into improvement initiatives
Conclusion
The landscape of AI quality metrics is vast and continuously evolving. While this comprehensive list provides a framework for evaluation, the key to success lies in selecting the right combination of metrics for your specific use case, implementing robust monitoring infrastructure, and maintaining a culture of continuous improvement.
Enterprises that invest in comprehensive AI quality measurement will not only deliver better user experiences but also build more trustworthy, reliable, and valuable AI systems that drive sustainable business growth.
Remember: what gets measured gets managed. By monitoring these diverse quality dimensions, organizations can ensure their AI systems meet the highest standards of performance, safety, and business value.


Leave a reply to McNeely Cancel reply