Overview of Copilot in Power BI
Imagine asking your data a question in plain English and getting an instant, accurate answer. That’s the promise of Power BI Copilot as a generative AI assistant that can transform how users interact with business intelligence. Rather than clicking through menus or building complex queries, users can simply type “What were our top performing products last quarter?” and receive immediate insights.
But there is a catch, and that is Copilot is only as good as the data it works with. When semantic models are poorly structured or lack proper context, the AI struggles to interpret questions correctly, leading to generic, inaccurate, or misleading responses. The quality of Copilot’s output hinges entirely on how well developers prepare their data models.
Power BI Copilot enables users to create and consume semantic models through natural language interactions, making analytics accessible to everyone in an organization, and not just data professionals. However, to unlock this potential, developers must invest time in proper model preparation and leverage Microsoft’s new “Prepare Data for AI” features.
Best Practices for Power BI Data Analyst to Enhance Copilot Accuracy

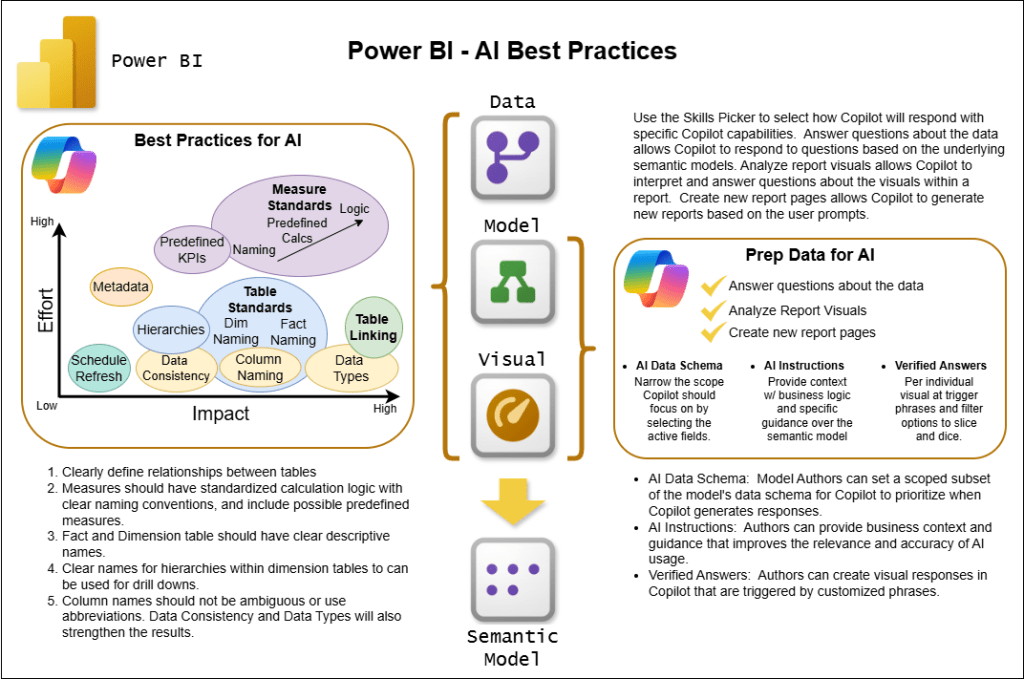
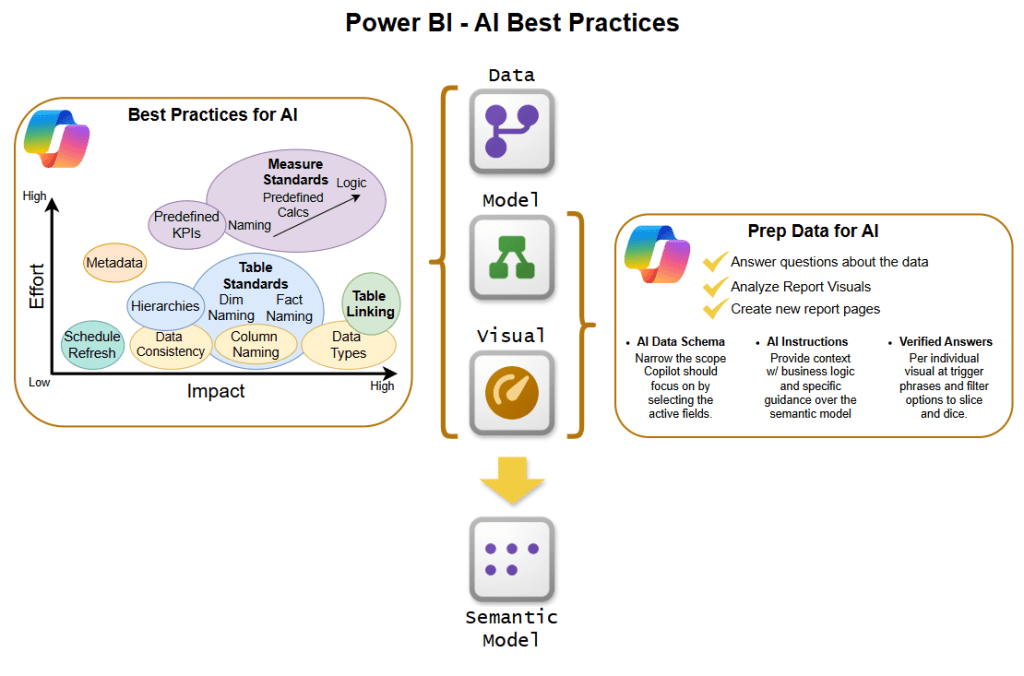
Before diving into specialized AI features, developers must ensure their semantic models follow fundamental best practices. Think of this as building a solid foundation before adding advanced capabilities.
Start with Model Design Fundamentals
Adopt a Star Schema architecture. This proven design pattern simplifies relationship structures by connecting a central Fact Table to dimension tables, making it dramatically easier for Copilot to navigate between related data. Complex, snowflake-style schemas can confuse the AI and lead to poor results.
Use human-readable naming conventions. Your table and column names should reflect how people actually talk about data in your organization. Instead of “CUST_ID” or “TBL_SALES,” use “Customer ID” and “Sales Transactions.” Copilot relies on matching natural language phrases to field names, so clarity is paramount.
Eliminate naming ambiguity. If you have a “Name” column in both your Customer table and your Store table, distinguish them clearly as “Customer Name” and “Store Name.” Duplicate field names across tables create confusion for both Copilot and users.
Enrich Your Model with Metadata
Write comprehensive descriptions for every object. Take time to document tables, columns, and measures with descriptive sentences explaining their meaning and purpose. These descriptions help Copilot generate narrative summaries and respond accurately to natural language queries. For example, a “Revenue” measure should include context like “Total revenue calculated from all closed sales, excluding returns and discounts.”
Create and document key business measures. Don’t force Copilot to figure out complex aggregations on the fly. Instead, define critical measures like “Total Sales,” “Year-over-Year Growth,” and “Customer Lifetime Value” directly in your model. Copilot excels at referencing predefined measures but struggles with creating complex calculations from scratch.
Hide irrelevant fields strategically. Not every column needs to be visible to Copilot. Hide technical fields like sort helpers, unique identifiers, or internal flags that don’t contribute to business analysis. This reduces noise and helps the AI focus on what matters.
Establish Clear Relationships and Rules
Define explicit relationships between tables. Copilot needs crystal-clear guidance on how data connects. Ambiguous or missing relationships lead to incorrect joins and nonsensical results.
Standardize calculations across the organization. If “Sales” means something specific in your business e.g. net of returns and including tax. Then make sure that definition is consistently applied in your measures. Document these business rules so Copilot can incorporate them into its responses.
Enable Q&A on your semantic model. This is a prerequisite for Copilot functionality. Without Q&A enabled, users won’t be able to leverage natural language queries at all.
Benefits of Adding ‘Prepare Data for AI’ Features in Power BI
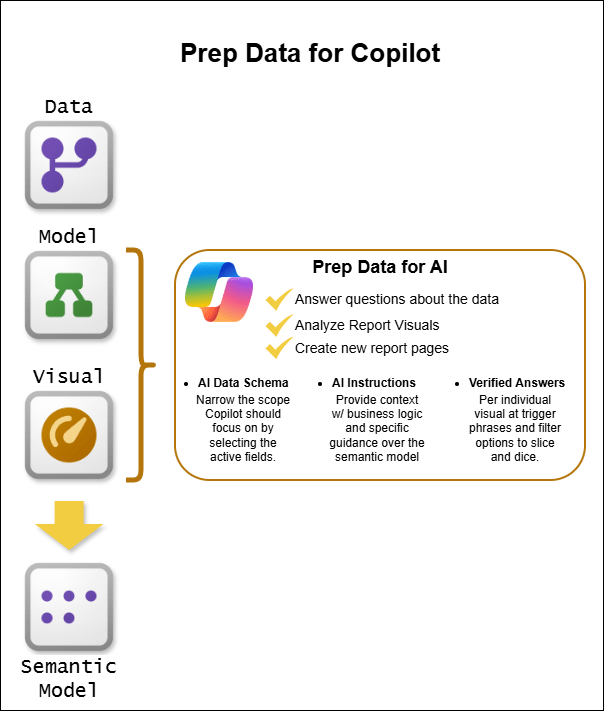
Microsoft has introduced three powerful features specifically designed to optimize semantic models for Copilot. Together, these tools transform good models into exceptional AI-ready data assets.
AI Data Schema: Simplify What Copilot Sees
Think of the AI Data Schema as creating a curated view of your model specifically for Copilot. While your full semantic model might contain hundreds of fields for various technical purposes, the AI doesn’t need to see everything.
This feature allows you to define which tables, fields, and relationships are most relevant for natural language analysis. For instance, you might exclude technical columns like row identifiers, surrogate keys, or audit timestamps that serve database functions but don’t answer business questions.
The benefit? Copilot can focus on the data that actually matters for analysis, reducing ambiguity and improving response times. It’s like giving the AI a simplified map instead of overwhelming it with every street, alley, and footpath.
Verified Answers: Guarantee Consistency and Accuracy
Verified Answers is your quality control mechanism. This feature lets you link specific questions to pre-approved visuals, ensuring that when users ask common questions, they receive human-vetted responses every single time.
For example, if users frequently ask “What are our quarterly sales trends?” you can set up trigger phrases that return a specific, verified visualization showing exactly that information. When someone asks one of these trigger phrases, Copilot delivers your pre-approved answer rather than generating a new response that might vary in quality or interpretation.
The benefits are substantial:
- Consistency across the organization: Everyone gets the same answer to the same question
- Human oversight on critical metrics: Your most important insights are reviewed and approved before reaching users
- Reduced risk of misinterpretation: Complex business logic is captured once and reused correctly
- Faster response times: Pre-vetted answers load quickly without requiring real-time AI generation
AI Instructions: Teach Copilot Your Business Language
AI Instructions might be the most powerful feature of all. This capability allows you to provide business context, terminology, and analytical guidance directly within your semantic model. You’re essentially training Copilot on how your organization thinks about data.
Effective AI Instructions should include:
Business terminology definitions: “When users mention ‘churn,’ they’re referring to customers who haven’t made a purchase in 90 days.”
Analysis preferences: “Always analyze sales data on a quarterly basis unless the user specifically requests monthly or annual views.”
Data prioritization rules: “For questions about retail performance, prioritize the Customer Segmentation and Sales Channel tables over raw transaction data.”
Clarification triggers: “When users ask about ‘product sales,’ always request clarification about which region or time period they’re interested in.”
Because AI Instructions rely heavily on prompt engineering, being specific and clear is essential. The more context you provide, the better Copilot understands user intent and delivers accurate, relevant insights.
Once your model passes testing, mark it as “Prepped for AI” in the Power BI service settings. This designation removes friction warnings for end users and signals that your model is ready for production AI interactions. Models marked as prepped for AI provide seamless experiences, while unprepared models display warnings that answer quality might be low.
Conclusion
Power BI Copilot represents a fundamental shift in how organizations interact with data, but only when developers lay the proper groundwork. By following semantic model best practices and leveraging Prepare Data for AI features, you create the foundation for high-quality, context-aware AI experiences.
The investment pays dividends across your organization. Users gain confidence in AI-generated insights. Decision makers access accurate information faster. Data literacy expands as natural language makes analytics accessible to non-technical staff. And your data governance improves through verified answers and standardized business logic.
Remember that AI behavior is nondeterministic and Copilot won’t produce identical responses every time, even with the same input. This makes human oversight through Verified Answers and clear guidance through AI Instructions even more critical. Your role as a developer isn’t to control every possible interaction but to provide the context, structure, and guardrails that enable Copilot to succeed.
Microsoft Power BI Copilot Links
Prepare Your Data for AI – Power BI | Microsoft Learn
Optimize Your Semantic Model for Copilot in Power BI – Power BI | Microsoft Learn

Leave a comment