The gap between those who can extract insights from data and those who need insights has long been one of technology’s most persistent challenges. Database administrators and developers speak SQL; business users speak strategy. This disconnect often means valuable data-driven decisions are delayed, opportunities are missed, and innovation is stifled by the simple inability to ask a database the right questions.
Enter the Model Context Protocol (MCP) an open standard that’s changing the game by enabling AI agents to interact with your data infrastructure using natural language. Microsoft’s implementation of MCP for SQL Server and Fabric represents more than just another developer tool. It is a bridge that finally connects business intent with technical execution.
What MCP Means for Your Organization
Think of MCP as a universal translator between AI assistants and your data systems. Just as you might ask Alexa about the weather or Siri to set a reminder, MCP allows you to ask your database complex questions in plain English and get meaningful, accurate answers back.
For example, instead of writing:
SELECT TOP 10 CustomerName, SUM(OrderTotal)
FROM Orders
WHERE OrderDate >= DATEADD(month, -3, GETDATE())
GROUP BY CustomerName
ORDER BY SUM(OrderTotal) DESC
You simply ask: “Show me our top 10 customers by revenue over the last three months.”
The AI agent, powered by MCP, understands your intent, translates it into the appropriate query, executes it securely, and presents the results in seconds.
The Business Case: Speed, Accessibility, and Innovation
Faster Time to Insight
In today’s business environment, the speed at which you can ask questions of your data often determines competitive advantage. With MCP enabled systems, business analysts no longer need to submit tickets to IT, wait for custom reports, or learn complex query languages. They can explore data interactively, iterate on questions, and discover insights in real-time conversations with AI assistants.
Democratized Data Access
When only a small percentage of your organization can effectively query databases, you’re operating with a fraction of your potential analytical capacity. MCP expands the circle of who can work with data meaningfully. Product managers can analyze customer behavior patterns. Operations teams can investigate supply chain bottlenecks. Sales leaders can segment territories and no one needs SQL expertise.
Innovation Through Iteration
Perhaps most importantly, natural language access encourages experimentation. When the barrier to asking questions is lowered, people ask more questions. They follow curiosity down unexpected paths. They discover patterns and opportunities that structured reporting might never reveal.
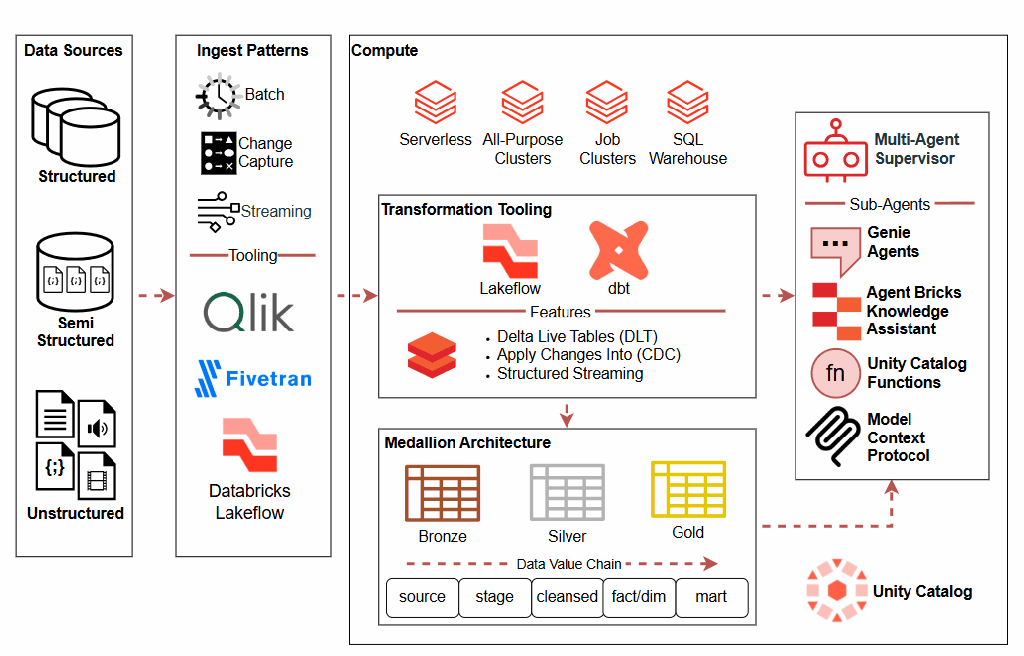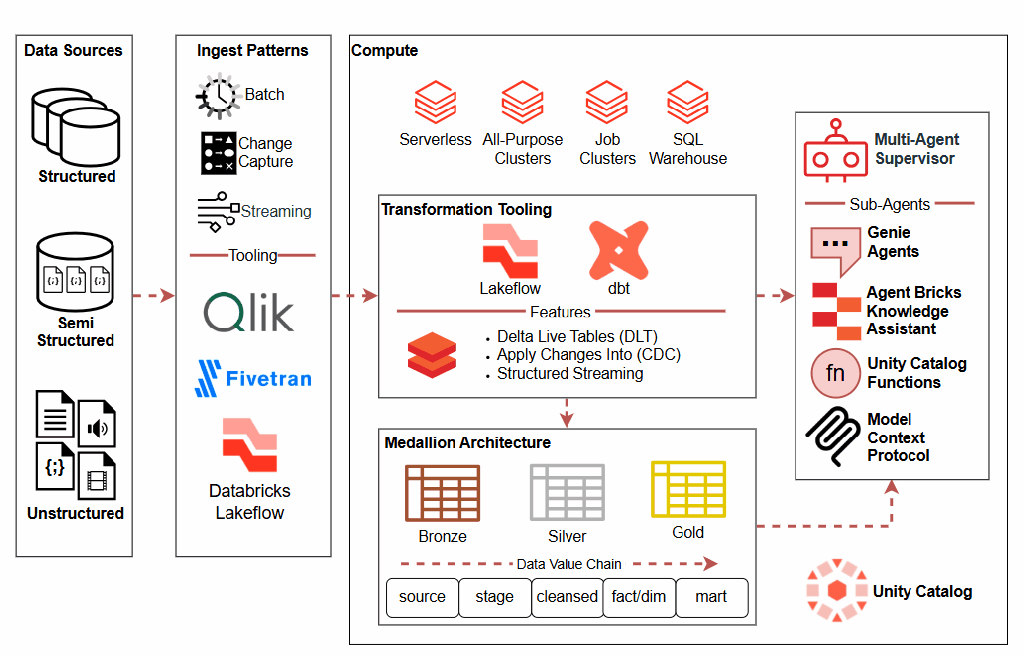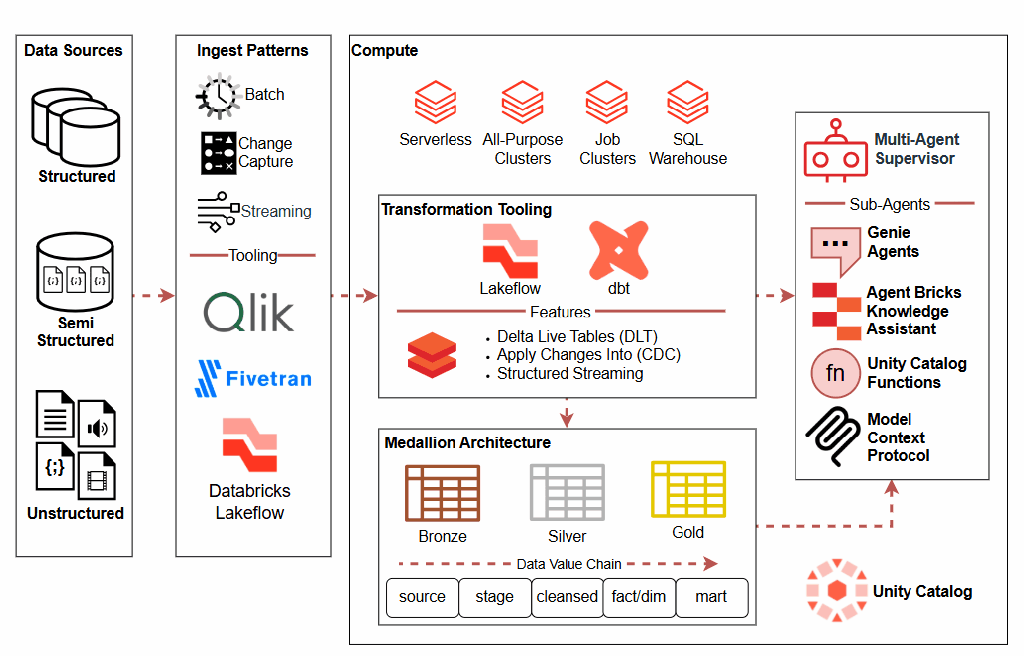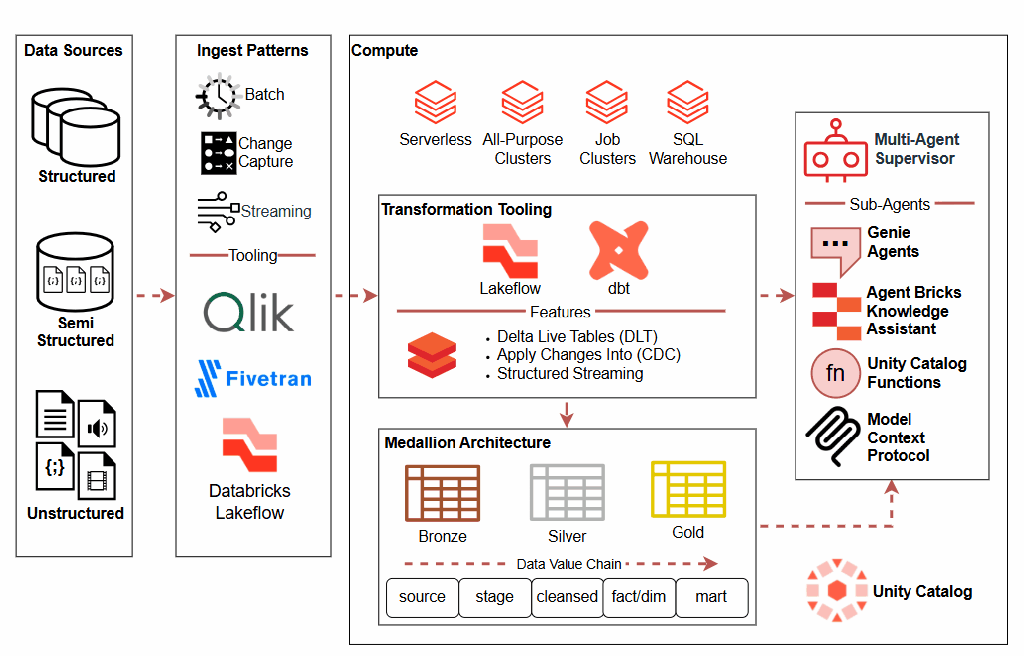
The Technical Foundation: Three MCP Implementations
Microsoft has released three complementary MCP implementations, each serving distinct technical needs:
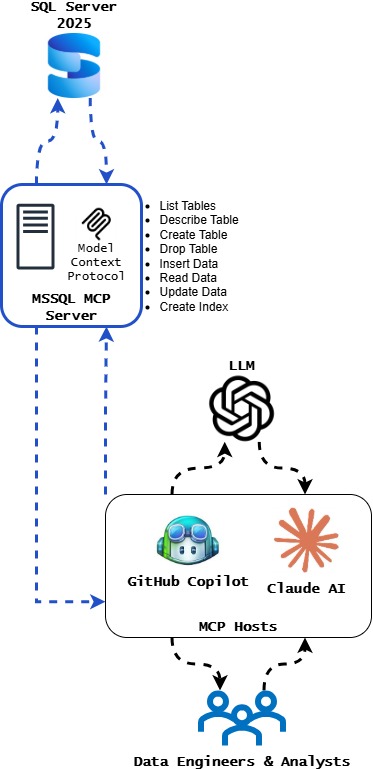
1. MSSQL MCP Server: Conversational Database Management
The MSSQL MCP Server transforms how teams interact with SQL Server databases, and SQL Database in Microsoft Fabric. Available in both .NET and Node.js implementations, it provides:
Schema Management Tools:
- List and describe tables with complete metadata
- Create new tables through natural language instructions
- Safely drop tables with built-in confirmations
Data Operations:
- Insert data with batch support for efficiency
- Query data without writing SELECT statements
- Update records based on natural language conditions
Performance Optimization:
- Create indexes to improve query performance
This server integrates seamlessly with Visual Studio Code (via GitHub Copilot) and Claude Desktop, using Entra authentication to ensure enterprise-grade security. Developers can switch between on-premises, Azure, and Fabric environments with simple connection string changes.
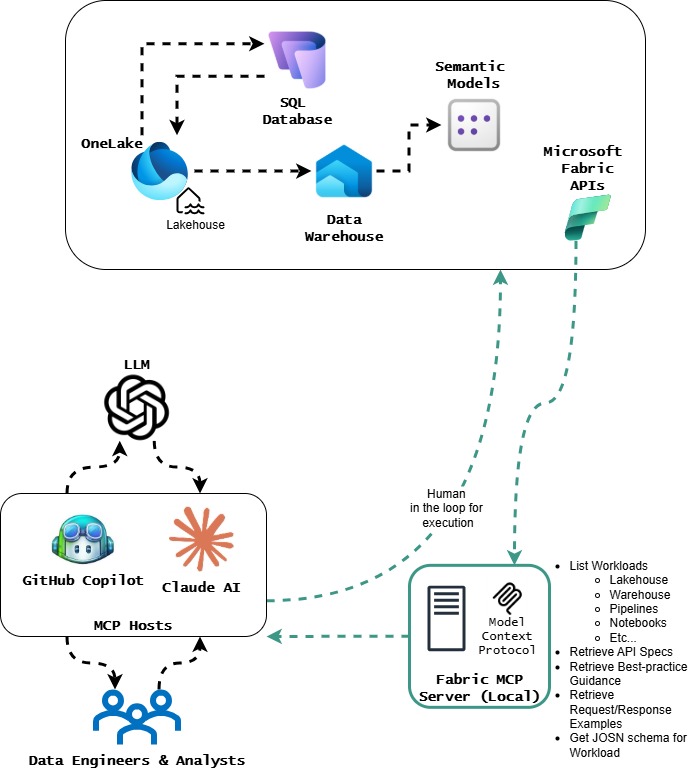
2. Fabric MCP Server: API-Powered Development
The Fabric MCP Server takes a different approach—it’s a local, developer-focused tool that packages Microsoft Fabric’s OpenAPI specifications, schema definitions, and best practices into an AI-accessible format.
This server runs entirely on your local machine, meaning:
- No production credentials at risk
- Offline access to complete API documentation
- AI agents can generate Fabric integration code with proper patterns
- Developers review and control what gets executed
Think of it as giving your AI coding assistant a comprehensive reference manual for Fabric APIs, complete with examples and security best practices.
3. Fabric Real-Time Intelligence (RTI) MCP Server: Live Analytics
For organizations working with real-time data, the Fabric RTI MCP Server bridges AI agents with Eventhouse and Azure Data Explorer using KQL (Kusto Query Language).
Eventhouse/Kusto Capabilities:
- Execute KQL queries through natural language
- List and explore databases, tables, and schemas
- Sample data for exploration and testing
- Ingest data directly into tables
- Get AI-powered query suggestions based on semantic similarity
Eventstream Management:
- List and explore Eventstreams in your workspace
- Retrieve detailed configuration and definitions
- Monitor real-time data flows

Technical Architecture: How It Works
At its core, MCP uses a client-server architecture:
- MCP Host: The environment running your AI model (like GPT-4 or Claude)
- MCP Client: An intermediary service (like GitHub Copilot or Claude Desktop) that forwards requests
- MCP Server: Lightweight applications exposing database capabilities as “tools” the AI can discover and invoke
When you ask a question:
- The AI agent receives your natural language request
- It discovers available MCP tools and selects appropriate ones
- The MCP server translates your request into database operations
- Results return through the same chain, with the AI formatting them naturally
- You review and approve any data modifications before execution
Security is built into every layer. Authentication uses your existing enterprise credentials (Entra ID), operations respect your existing permissions, and write operations can be restricted or require explicit approval.
Real-World Scenarios
For Data Analysts: “Analyze sales trends across our top five product categories for Q3, broken down by region, and identify any unusual patterns.” The MCP server executes multiple queries, aggregates results, and the AI presents findings with context and recommendations.
For Developers: “Generate a Python script that connects to my Fabric lakehouse, reads the customer churn dataset, and creates a feature engineering pipeline.” The Fabric MCP Server provides accurate API calls, proper authentication patterns, and error handling all from a conversational prompt.
For Operations Teams: “Show me all Eventstreams processing IoT sensor data, their current throughput, and flag any that are experiencing delays.” The RTI MCP Server retrieves real-time status and presents actionable intelligence.
For Business Leaders: “Compare this quarter’s revenue to last year, highlight our fastest-growing customer segments, and identify products with declining sales.” Natural language access means strategic questions don’t require technical intermediaries.
Implementation Considerations
Security and Governance
MCP doesn’t bypass your existing security. Users can only access data they are already authorized to see. For production environments, consider:
- Implementing read-only modes where appropriate
- Setting up approval workflows for data modifications
- Auditing MCP interactions through existing logging infrastructure
- Starting with development environments before production rollout
Training and Adoption
While MCP lowers the technical barrier, effective data analysis still requires domain knowledge. Invest in training that helps users:
- Ask better questions of their data
- Understand what results mean in business context
- Recognize when to involve specialists for complex analyses
- Develop data literacy alongside AI literacy
Infrastructure Planning
Start with pilot projects that demonstrate value quickly:
- Choose high-impact, frequently-asked questions as initial use cases
- Deploy in development or analytics environments first
- Measure time savings and insight velocity
- Expand based on demonstrated ROI and user demand

The Path Forward
The Model Context Protocol represents a fundamental shift in how we think about data accessibility. It’s not about replacing data professionals. It is about amplifying their impact by handling routine queries and freeing them for complex analytical work. It’s about ensuring that everyone in your organization who needs data-driven insights can get them, regardless of their technical background.
As these tools move from preview to general availability, organizations that adopt MCP-enabled workflows early will develop competitive advantages: faster decision-making, broader analytical participation, and cultures where data curiosity is encouraged and easily satisfied.
The future of data isn’t just about having more of it. It is about making it conversationally accessible to everyone who needs it. Model Context Protocol is helping build that future.


Leave a comment